Category: Vocabulary
-

Spelling English Word vocabulary with Bengali meaning
ইংরেজি শব্দের বানান-রীতি ও কৌশলবানান মনে রাখার সহজ উপায় হলো যখন শব্দটি পড়বেন তখন বানানটিও মনোযোগ দিয়ে দেখে নিতে হবে সবচেয়ে ভালো হয় কয়েকবার syllable ভাগ করে পরা ও লেখা । কিছেু কৌশল আছে যেগুলো সহজেই আয়ত্ত করা যাবে।নিচে সেই রকম কিছু কম কৌশল দেওয়া হলRule-1: ‘l’ দ্বারা গঠিত এক syllable বিশিষ্ট শব্দে যদি ‘l’ এর পূর্বে একটিমাত্র vowel থাকে, তাহলে এ শব্দের শেষে ‘ll’ ব্যবহার করতে হয়। যেমন: Well, tell, fill till.Rule-2: ‘l’ দ্বারা সমাপ্ত এক syllable বিশিষ্ট শব্দে যদি ‘l’ এর পূর্বে দুইটি vowel থাকে, তাহলে ঐ শব্দের শেষে একটি ‘l’ ব্যবহার করতে হয়। যেমন: Feel, weal, meal, goal.Rule-3: Consonat যুক্ত কোনো suffix (ness ব্যতীত) যদি ‘ll’ দ্বারা সমাপ্ত হয়ে এক syllable বিশিষ্ট কোনো শব্দের শেষে যুক্ত হয়, তাহলে শেষের ‘l’ বাদ যাবে।যেমনঃ Well+come=welcome; well+fare=welfare; full+fil=fulfil.কিন্তু vowel যুক্ত Suffix হলে ‘ll’ ই ব্যবহার করতে হবে। যেমন: ill+ness=illness.Rule-4: ‘ll’ দ্বারা সমাপ্ত এক syllable বিশিষ্ট শব্দ যদি suffix হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হয়, তাহলে শেষের ‘l’ বাদ দিতে হবে।যেমনঃ roll-enrol, fill-fulfil, full-doubtful etc.Rule-5: কোনো শব্দের শেষে যদি একটি consonant থাকে এবং consonant টির পূর্বে যদি একটি vowel থাকে এবং এরপর আদিতে যদি vowel বিশিষ্ট কোনো suffix (প্রত্যয়) যুক্ত হয়, তাহলে শেষের consonant টি দ্বিত্ব (double)হবে। যেমন: concel+ed=cancelled, travel+er=traveller.ব্যতিক্রমঃ Benefited, credited, differed, galloped, paralleled, visitor.Rule-6: যে সমস্ত word এর শেষে ‘y’ থাকে এবং সেই ‘y’ এর পূর্বে যদি consonant থাকে তাহলে i বিশিষ্ট প্রত্যয় (ing+ist) বাদে অন্যান্য প্রত্যয় যুক্ত করার সময় ‘y’ এর স্থানে ‘i’ হয়। যেমন: Accompany=Accompaniment, Busy=Business.Rule-7: দুই বা তিন syllable যুক্ত word এর শেষে যুদি একটি consonant এবং তার আগে যদি একটি vowel থাকে এবং উচ্চারণের সময় যদি শেষ syllable এ stress পড়ে তাহলে সেক্ষেত্রে কোনো suffix যোগ করতে হলে শেষ Consonant টি double (দ্বিত্ব) করতে হয়।যেমনঃ begin+er=beginner, swim+ing=swimming.কিন্তু stress যদি প্রথম syllable এর উপর দেওয়া হয়, তাহলে Consonant টি double হয় না।যেমনঃ Murmur+ed=murmured, orbit+ing=orbiting.Rule-8: কোনো শব্দের শেষে যদি ‘y’ থাকে এবং তার পূর্বে যদি কোনো vowel থাকে, তাহলে সেই শব্দের সাথে কোনো suffix যোগ করার সময় সাধারণত ‘y’ এর কোনো পরিবর্তন হয় না।যেমনঃ Buy=Buyer, Boy=Boyish, Journey=Journeyed ইত্যাদি।ব্যতিক্রমঃ Say=said, Day=Daily ইত্যাদি।Rule-9: শব্দের শেষে যদি ‘y’ থাকে এবং সেই ‘y’ এর পূর্বে যদি ‘t’ থাকে এবং তারপর যদি ‘ous’ যোগ করতে হয় তাহলে ‘y’ এর স্থলে e হয়।যেমনঃ Beauty=Beauteous, Pity=Piteous ইত্যাদি।Rule-10: যদি কোনো word এর শেষে ‘e’ থাকে এবং সে word এর প্রথমে যদি vowel বিশিষ্ট কোনো প্রত্যয় যুক্ত করতে হয়, তাহলে শব্দের শেষের ‘e’ সাধারণত বাদ দিতে হয়।যেমনঃ Come=Coming, Write=Writing. কিন্তু word এর শেষে ‘e’ এবং word টির পূর্বে যদি ‘g’ বা ‘c’ থাকে তাহলে সে word এর শেষে ‘ous’ এবং ‘abl’ যুক্ত করার সময় word এর শেষের ‘e’ বাদ যায় না। যেমনঃ Courage= Courageous, Charge=Chargeable.ব্যতিক্রমঃ Practice=Practicable.Rule-11: কোনো word এর শেষে যদি ee, oe বা ye থাকে তাহলে সে word এর শেষে ed বাদে প্রথমে যদি vowel বিশিষ্ট অন্য কোনো প্রত্যয় যুক্ত হয়, তাহলে শব্দের শেষের ‘e’ বাদ যায় না। যেমনঃ Agree=Agreeable, Free=Freeing, See=Seeing ইত্যাদি।Rule-12: যদি কোনো word এর শেষে ie থাকে, তবে সে word এর শেষে ing যোগ করতে হলে ie-এর স্থানে ‘y’ হয়।যেমনঃ Die=Dying, Tie=Tying ইত্যাদি।Rule-13: যদি কোনো word এর শেষে ‘e’ থাকে এবং সে word এর শেষে যদি consonant বিশিষ্ট কোনো প্রত্যয় যোগ করতে হয়, তাহলে ‘e’ বাদ যাবে। যেমনঃ Argue=Argument, Simple=Simple, Awe=Awful.ব্যতিক্রমঃ Achieve=Achievement. আবার কিছু কিছু word আছে যেগুলোতে e বাদ দিলেও চলে, না দিলেও চলে। যেমনঃ Abridge=Abridgment/Abridgement.Rule-14: কোনো word এ ব্যবহৃত ‘i’ এবং ‘e’ একত্রে থেকে যদি দীর্ঘ-ঈ (বা Double) এর মত উচ্চারিত হয়, তাহলে সাধারণত প্রথমে ‘i’ ব্যবহৃত হয় এবং পরে ‘e’ ব্যবহৃত হয়।যেমনঃ Achieve, belief, brief, chief, friend. ব্যতিক্রমঃ Conceive, Ceiling,Rule-15: কোনো word-এ ব্যবহৃত ‘i’ এবং ‘e’ যদি একত্রে থেকে দীর্ঘ-ঈ এর মতো উচ্চারিত না হয়, তাহলে সাধারণত প্রথমে ‘e’ এবং পরে ‘i’ ব্যবহৃত হয়। যেমনঃ Heir, Height.Rule-16: কিন্তু word এর পদান্তর (যেমন: Noun-Adjective) হলে মাঝে মাঝে ‘u’ বাদ দিতে হয়। যেমনঃ Honorary, Labour=Laborious.Rule-17: ইংরেজি ভাষায় কিছু শব্দ আছে যেগুলোকে পৃথক করে লেখা যায় না।যেমনঃ Anybody, Everybody, Elsewhere, Cannot, Instead, Nothing, Nowhere, Welcome, Sometimes, Nobody. -

British and American Words
British and American Words
Here you will know some British and American Words.
British English Meaning American English Hello! ওহে! Hi! Taxi ট্যাক্সি Cab Pub শুড়িখানা Bar Film চলচ্চিত্র Movie Hire ভাড়া Rent Holiday ছুটির দিন Vacation Lorry লরি Truck Underpants হাফ প্যান্ট Shorts Sweets মিষ্টি Candy Rubber রবার ঘর্ষক Eraser Lift লিফট Elevator Flat ফ্লাট Apartment Aerial বেতার সংকেত গ্রহনের তার Antenna Greengrocery সব্জি বা ফলের দোকান A fruit & vegetable store Trousers ট্রাউজার Pants Paraffin কেরোসিন তেল Kerosene Rubbish বাজে বস্তু Garbage Works কারখানা Factory Queue লাইন Line Petrol পেট্রুল Gasoline Luggage ভ্রমনকারীর মালপ্ত্র Baggage Bill হুন্ডি Cheque Timetable কার্যাদির সময় সূচি Schedule Windscreen মোটর গাড়ির কাচ Windshield Puncture ছোট ছিদ্র Blow-out Ok হ্যা/ঠিক আছে Sure All right হ্যা/ঠিক আছে Sure Yes হ্যা/ঠিক আছে Sure Tap কল Faucet Common confusing words.
There are a lot of common confusing words in English which are used in daily activities in our life. Sometimes we forget the use of correct rules of grammar. Here I will share with you the commonly confused words. Such as hear/listen, home/house, cool/cold, laugh/smile/giggle, hot/worm, sick/ill, breast/chest, finger/toe, dress/suit, glad/delighted।
1.কখন Hear/ কখন Listen:
মনোযোগ দিয়ে শোনা বুঝাতে Listen হবে আর সাধারণভাবে শোনা বুঝাতে hear হবে।Example: 1. Listen to me. 2.Jihad heard the news.
2. কখন Home/ কখন House:
Home বসবাসের উদ্দশ্যে ব্যবহৃত হয় আর house বসবাসের উদ্দশ্যে ও ব্যবসা-বানিজ্যে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
Example: 1. Juicy will go home next Friday. 2. We shall start grocery in the land house..
3. কখন Cool/ কখন Cold:
আরামদায়ক ঠান্ডাবুঝাতে cool আর কষ্টদায়ক ঠান্ডা বুঝাতে cold হয়।
Example: 1. A winter morning is cold. 2. Jihad always uses ice cool.
4. When Laugh/ when smile/ when Giggle ? (হাসা)।
মুচকী হাসলে smile, শব্দ করে হাসলে laugh আর মুখ চেপে হাসলে giggle হয়।
Example: 1. Shamim smiled.
5.When Hot /when Worm (গরম):
আরাম দায়ক গরম হলে Worm এবং কষ্টদায়ক গরম হলে hot হয়।
Example: We can not stay in the class in a hot day.Learn English New Way
Note : ব্যক্তি গরম হওয়া অর্থেও hot হয়। Example: Is anyone too hot? ( কেউ কি গরম/রাগান্বিত হয়েছে?
6.When sick/when ill ? (অসুস্থ )
অল্প সময়ের জন্য অসুস্থ হলে sick এবং দীর্ঘসময়ের জন্য অসুস্থ থাকলে ill হবে।
Example:1. Amal is in a sickbed. 2. The old man is suffering from illness for some years.
7.When Breast/ when Chest ?(বুক):
ছেলেদের বুক হলে Chest আর মেয়েদের বুক হলে Breast হবে.
Example: 1. The boy is suffering from chest pain. 2. The mother is suffering her breast to her child.
8. When Finger/ when Toe? (আঙুল):
হাতের আঙুল হলে Finger আর পায়ের আঙুল হলে Toe হবে.
Example: 1. Your fingers are neat and clean. 2. Your toes are burnt.
9. When Dress/when Suit? 9পোশাক):
Dress হচ্ছে মেয়েদের পোশাক আর Suit হচ্ছে ছেলেদের পোশাক।
Example: 1. Jakia wore her new dress.
2.Arman wore his new suit.
10.When Glad/ when Delighted? (আনন্দিত)
Glad মানে আনন্দিত । কিন্ত তার চেয়েও বেশী আনন্দিত বুঝাতে delighted হয়।
Example: 1. Rupok is glad. 2. Kona is delighted with her book.Phrase and Idioms.
1.A bed of roses
=আরামের স্থান
Heaven is a bed of roses.
2.A bed of thorns
= কষ্টের স্থান।
The hell is a bed of thorns.
3.A fish out of water
=অস্বস্তিকর অবস্থা।
I feel like a fish out of water in a new place.
4. A fool’s paradise
=বোকার স্বর্গ
The world is a fool’s paradise.
5. A jailbird
=আসামী
Saki is not a jailbird.
6. A laughing stock
=হাস্যকর ব্যক্তি/বিষয়
Dilder was a laughing stock.
7. At one’s wit’s end
=হতবুদ্ধি
Farid is at one’s wits end what to do?
8. A man of letters
=পন্ডিত ব্যক্তি
Biddasagar was a man of letters.
9. Bite your tongue
=চুপ হয়ে যাওয়া।
Sometimes, Rima needs to bite her tongue.
10. Pic in the sky
=আকাশ কুশুম কল্পনা।
It is a Pic in the sky.
11. Sleep tight
=ভালঘুম।
Saki, good night, sleep tight.
12. kick the bucket
= অকেজো হয়ে যাওয়া।
My old mobile kicked the bucket.
13. At deadlock
=অচল
Nowadays, five Paisa is at a deadlock.
14. A rainy day
= দুর্দিন
We should save something against rainy days.
15. At home
= আরাম।
Does Juicy feel at home.
16. A1
=ভাল
Smart Grammar is a A1 book.
17. Come true
=হত্য হওয়া।
One day my dream will come true.
18. heart and soul
=মনোযোগ।
I will try to love Allah heart and soul.
19. At every step
= পদে পদে
I faced problems at every step of my life.
20. Acid test
=কঠিন পরিক্ষা
It is an acid test for me.
21. Backwards and forwards
=সামনে-পিছনে
Jihad looks backwards and forwards.
22. At all times
=সবসময়
I can not help a man at all times.
23.At first
=প্রথমে
At first, I did not see her.
24. A man of word
=এক কথার লোক।
Rashed is a man of word.
25. A close fisted man
=কৃপণ লোক
All hate close fisted man.
26. Breath one’s last
=My grandfather breathed his last.
27. Call attention
=মনোযোগ আকর্ষণ করা
The students called attention to their teacher.
28. Cart before the horse
= বিশৃংখলা
To act illogically is to put the cart before the horse.
29. Break one’s heart
=কষ্ট দেওয়া।
The sad news broken my heart.
30. Begger description
=বর্ননাতীত
His sufferings begger description. -

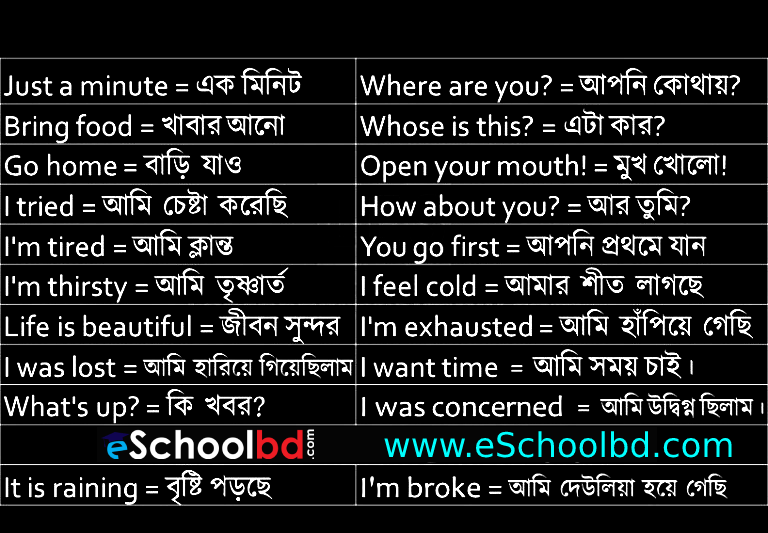
Spoken English practice 06
1..A long time ago অনেক দিন আগের কথা।
2..A one day ticket একদিনের টিকেট।
3.A few কিছু।
4.A little কিছু ।
5.A round trip ticket যাওয়া আসার টিকেট ।
6. About 2oo kilometers প্রায় ২০০ কিমি।
7. Across from the post office পোস্ট অফিসের বিপরীতে।
8. All day সারাদিন ।
9. All seems yellow to the jaundice eye চক্ষু মন্দ তো জগৎ মন্দ
10. Am I pronouncing it correctly? আমি কি সঠিক উচ্চারন করেছি?
11. Juicy is Rupu’s girlfrind জুইসি রুপুর বান্ধবী।
12. And you?আর তুমি?
13. Anything else?আর কিছু?
14. Is there any concerts? কোন গানের অনুষ্ঠান আছে?
15.Are they coming this evening?তারা কি আজ সন্ধ্যায় আসছে?
16.Are the the same? তারা কি একই রকম?
17.Are you afraid? তুমি কি তুমি ভীত?
18.Are you allergic to anything? তুমার কোন বিষয়ে স্পর্শকাতরতা আছে?
19.Are you Bangladishi? তুমি কিবাংলাদেশি?
20. Are you comfortable?তুমি কিআরামবোধ করছ?
21.Are you free tonight? আজ রাতে তুমার সময় হবে?
22.Are you getting me ? আমার কথা কি বুঝতে পারছ?
23.Are you going to attend their wedding? তুমি ওদের বিয়ের অনুষ্ঠানে যোগ দিচ্ছ?
24.Are you going to help her? তুমি কি মেয়েটিকে সাহায্য করছ?
25. Are you going to take a plan or train? তুমি প্লেন নাকি ট্রেন এ যাবে?
26.Are you here alone? এখানে কি তুমি একা?
27.Are you hungry? তুমি কি ক্ষুধার্থ?
28 Are you married? তুমি কিবিবাহিত?
29 Are you okay? তুমি ঠিক আছ তো ?
30 Are you ready ?তুমি কিপ্রস্তুত?
31. Are you sick?তুমি কিঅসুস্থ?
32 Are you sure?তুমি কি নিশ্চিত?
33 Are you waiting for someone? তুমি কারো জন্য অপেক্ষা করছ?
34 Are you working today? আজ কি কাজ করছ?
35 Are you working tomorrow? কাল কি কাজ করবে?
36 Are your children with you? তোমার বাচ্চারা কি তোমার দাথে?
37 As soon as possible যত তাড়াতাড়ি সম্ভব।
38 At 3 o’clock. ৩ টায়
39At 3 o’clock. in the afternoon বিকাল ৩ টায়
40 At 5th street ৫ নম্বর রাস্তায়।
Is this article useful yes or no? -

Spoken English 04
Spoken English Part -1(Translations)
Be careful= সাবধান থাকবেন।
Be careful driving = সাবধানে গাড়ি চালান।
Be off now=এখন বিদায় হও।
Be quiet= শব্দ করোনা।
Be sincere about your son= তোমার ছেলের ব্যাপারে যত্নবান হও।
Behind the bank=ব্যাংকের পিছনে।
Birds of a feather, flock together=চোরে চোরে মাসতু ভাই।
Bring me my shirt please=অনুগ্রহ করে আমার শার্টটা এনে দাও।
Bullshit=যত্তোসব
Business is good= ব্যবসা ভাল যাচ্ছে।
Call me= ফোন করো।
Call the police= পুলিশ ডাক।
Can I access the internet here?এখানে ইন্টানেট ব্যবহ্রার করতে পারি?
Can I borrow some money?কিছু টাকা ধার পেতে পারি?
Can I bring my friend?আমার বন্ধুকে কি সাথে আনব?
Can I have a glass of water please?অনুগ্রহ করে আমাকে এক গ্লাস পানি দিতে পারবেন?
Can I have a receipt please ? অনুগ্রহ করে আমাকে একটি রশিদ দেবেন?
Can I help you?তোমাকে সাহায্য করতে পারি?
Can I make an appointment for next Wednesday?আগামি বুধবারে সাক্ষাতের জন্য সময় ঠিক করতে পারি?
Can I see your passport please ? অনুগ্রহ করে আপনার পাসপোর্ট দেখতে পারি?
Can I take a message ?আমি কি একটি বার্তা রেখে যেতে পারি?
Can I try it on ? আমি কি এটা পরে দেখতে পারি?
Can I use your phone ? আমি কি আপনার ফোন ব্যবহ্রার করতে পারি?
Can it be cheaper? এটা কি দামে সস্তা?
Can we have a menu please?আমরা কি একটি মেনু পেতে পারি?
Can we have some more bread please? অনুগ্রহ করে আমাদের আরো কিছু রুটি দিবেন?
Can we sit over there?আমরা কি এখানে বসতে পারি?
Can you call back later?আপনি কি পরে ফোন করবেন?
Can you call me back later?আপনি কি আমাকে পরে ফোন করবেন?
Can you carry this for me?আপনি কি এটা আমার জন্য বইবেন?
Can you do me favor?অনুগ্রহ করে সাহয্য করবেন?
Can you fix this?আপনি এটা ঠিক করতে পারবেন?
Can you give me an example?আপনি একটা উদাহারন দিতে পারবেন?
Can you guess what I’m gonna tell me?ভাবতে পারো এখন আমি তুমাকে কি বলব?
Can you help me? আপনি কি আমাকে সাহায্য করতে পারেন?
Can you hold this for me ?অনুগ্রহ করে আমার জন্য এটা ধরে রাখবেন?
Can you please say that again?দয়া করবেন বিষয়টি আরেকবার বলবেন?
Can you recommend a good restaurant? আমাকে একটি ভাল রেস্টুরেন্টের ঠিকানা দিবেন?
Can you repeat that please? অনুগ্রহ করে বিষয়টি পুনরাবৃত্তি করবেন?
Can you show me?তুমি আমাকে দেখাতে পার?
Can you speak louder please? অনুগ্রহ করে আর একটু জোরে বলবেন?
Can you swim?তুমি সাতার জান?
Can you throw that away for me?তুমি কি এটা আমাকে ছুরে দেবে?
Can you translate this for me ?তুমি কি এটা আমার জন্য অনুবাদ করতে পার?
Certainly!নিশ্চয়!
Cheers!উপভোগ কর!
Dhaka is very different from Sherpur. ঢাকা থেকে শেরপুর একেবারেই আলাদা।
Come here.এখানে আস।
Confine in me?আমাকে বিশ্বাস করো।
Converse is the case?আসলে ব্যাপার টা উলটো।
Convey my words to him আমার কথাটা তাকেবল।
Is this article useful yes or no?
For next post ,please comment.
Thank you to all. -

Law Words – আইন সম্পর্কীয় শব্দাবলি
আইন সম্পর্কীয় শব্দাবলি
Witness = ( উইটনেস ) সাক্ষী
Case = ( কেস ) মামলা
Evidence = ( এভিডেন্স ) প্রমান
Oath = ( ওথ ) শপথ
Plaint = ( প্লেইন্ট ) আরজি
Hearing = ( হেয়ারিং ) শুনানি
Deposition = ( ডিপোজিশন ) জবানবন্দি
Document = ( ডকুমেন্ট ) দলিল
Bail = ( বেইল ) জামিন
Accused = ( একিউজড ) আসামি
Offence = ( অফেন্স ) অপরাধ
Murder = ( মার্ডার ) খুন
Appeal = ( আপিল ) আপিল
Law = ( ল ) আইন
Plaintif = ( প্লেনটিফ ) বাদী
Defendant = (ডিফেনডেন্ট ) বিবাদী
Assault =(এসাল্ট) আক্রমণ
Bribe =(ব্রাইব) ঘুষ খাওয়া
Thift = (থিফট) চুরি
Rape = (রেপ) ধর্ষণ
Hanging = ( হ্যাংগিং) ফাঁসি
Robber = ( রোবার) ডাকাত
Imprisonment = (ইমপ্রিজনমেন্ট) কারাদণ্ড
Acquittal = ( একুইটাল) খালাস
Dock = (ডক) কাঠগড়া
Judgement = (জাজমেন্ট) রায়
Punishment = ( পানিশমেন্ট) শাস্তি
Contract = ( কন্ট্রাক্ট) চুক্তি
Lockup = (লক আপ) হাজত
Court =(কোর্ট) আদালত
High court = (হাইকোর্ট) উচ্চ আদালত
Advocate = (এ্যাডভোকেট) উকিল
Client = (ক্লাইয়েন্ট) মক্কেল
Justice = (জাস্টিস) বিচার পতি
Homicide = (হোমিসাইড) নরহত্যা
Suicide = (সুইসাইড) আত্মহত্যা
Claim = ( ক্লেইম) দাবি
Warrant = (ওয়ারেন্ট) গ্ৰেফতারী
Civil court = (সিভিল কোর্ট) দেওয়ানী আদালত
Chief justice = (চীফ জাস্টিস) প্রধান বিচারপতি
Release = ( রিলীজ) মুক্তি
Handcuff = ( হ্যাণ্ড কাফ) হাতকড়া
Fine = (ফাইন) জরিমানা -

English Vocabulary ইংরেজি শব্দ ভান্ডার
English Vocabulary
ইংরেজি শব্দ ভান্ডার
আজকে আমরা শিখবো এমন কিছু ইংরেজি শব্দ যেগুলোর সাথে কিছু অংশ যোগ করলে আলাদা অর্থ হয়ে যায়। এইভাবে আমাদের পরিচিত শব্দের সাথে মিলিয়ে পড়লে সহজেই মনে থাকবে।
Late -দেরি ; Lately- সাম্প্রতিক,
Kin- আত্মীয়; Akin -সদৃশ,
Tract- বিস্তার; Extract- নির্যাস,
Peal- পর পর উচ্চ শব্দ; Repeal-বাতিল করা,
Act- আইন ; Exact -সঠিক,
Test- পরীক্ষা ; Detest -ঘৃণা করা,
Tent- তাবু ; Latent -সুপ্ত,
Novel-উপন্যাস; Novelty- নতুনত্ব,
For- জন্য; Forgo- পরিত্যাগ করা,
Can -পারা; Candid-অকপট,
Cure-আরোগ্য; Procure- রাজি করান,
Desperate- হতাশ; Desperately গুরুতরভাবে,
Stick লাঠি; Sticky আঠালো,
Heek- নরক; Heekly- ব্যাহত করা,
Ease- আরাম; Cease- থামা,
Appropriate- যথাযথ; Misappropriate- আত্মসাৎ করা ,
Film- চলচ্চিত্র; Filmy- হালকা পাতলা,
Set- চালু করা; Outset- আরম্ভ,
Pair- জোড়া; Impair- দুর্বল,
Face- মুখ; Efface- ঘষে তুলে ফেলা,
Grave- সমাধি; Engrave- খোদাই করা,
Cape- অন্তরীপ; Escape- পালিয়ে যাওয়া,
Muse- গভীর চিন্তা করা ; Amuse- আনন্দ দান করা,
Ride- ঘোড়ায় চড়া; Deride- হাসিঠাট্টা করা,
Cite- উদাহরণ দেওয়া; Incite- উত্তেজিত করা,
Motion- গতি; Commotion- মানসিক বিপর্যয়,
Sloven- অপরিচ্ছন্ন; Slovenly- অমনোযোগী,
Over- শেষ; Overt- প্রকাশ্য,
Bust- বক্ষ; Robust- বলবান,
File- নথি; Defile- দৃষিত করা,
Fusion- গলিয়ে মিশ্রন; Profusion-সমৃদ্ধি,
Treaty- চুক্তি; Entreaty- প্রার্থনা,
Treat- আচরন করা; Retreat- পিছু হটা.
-

Phrases & Clause
Phrases & Clause
Clause Definition:
A clause is referred to as a group of words that has a subject and a predicate and acts as a part of a complex or compound sentence.
Clause একটি শব্দগুচ্ছ যার একটি subject (উদ্দেশ্য) এবং একটি predicate (বিধেয়) আছে এবং যা একটি complex অথবা একটি compound sentence এর অংশ হিসেবে কাজ করে ।
Example:
When the girl was singing, we were listening to her.
Here the sentence has two clauses, “When the girl was singing” and “we were listening to her”, each having a subject and a predicate.
এখানে sentence টির দুটি clause আছে, “When the girl was singing” এবং “we were listening to her”, প্রতিটিরই একটি subject (উদ্দেশ্য) এবং একটি predicate (বিধেয়) আছে ।
Types of Clause:
Clauses are mainly of two types:Clause প্রধানত: দুই প্রকার:
Independent Clauses (Main Clause)
Dependent Clause (Subordinate Clause)
Dependent Clause can be again divided into three types.Dependent Clause কে আবার তিন ভাগে ভাগ করা যায়।:
Noun Clause.
Adjective or Relative Clause.
Adverb Clause
Adjective বা Relative Clause কে আবার দুই ভাগে ভাগ করা যায়।:Restrictive Clause
Nonrestrictive Clause
All types of clauses are discussed below.:নিচে সবধরনের clause বর্ণিত হল।
Independent Clauses (Main Clause):
An independent clause is a clause which has a complete meaning and can stand alone as a sentence. Simple sentences are independent clauses.একটি Independent Clause হলো এমন একটি clause যার একটি পূর্ণ অর্থ আছে এবং যা একাই একটি sentence হিসেবে দাঁড়াতে পারে । Simple sentence গুলোই হল independent clause ।
Example:
The University is closed today.
I am going out for a vacation.
She is studying very hard.
All the simple sentences above are independent clauses because all have complete meanings and stand alone as sentences.উপরের সব simple sentence গুলোই independent clauses কারণ সবারই পূর্ণ অর্থ আছে এবং পৃথকভাবে sentence হিসেবে দাঁড়াতে পারে ।
Dependent Clause (Subordinate Clause):
Subordinate or dependent clauses refer to the type of clauses that depend on an independent clause to express a complete meaning and cannot stand alone as a sentence. These clauses start with a dependent word like a relative pronoun or a subordinate conjunction. Such as, who, because, and, but, although, where, when, etc.একটি dependent clause হল এমন একটি clause যা একটি পূর্ণ অর্থ প্রকাশ করতে একটি independent clause এর উপর নির্ভর করে এবং একটি পৃথক sentence হিসেবে দাঁড়াতে পারে না । এই clause গুলো একটি নির্ভরশীল শব্দ তথা একটি relative pronoun অথবা একটি subordinate conjunction দিয়ে শুরু হয় । যেমন: who, because, and, but, although, where, when, প্রভৃতি।
Example:
The writer who came here was my friend.
When the rain stopped, we started our journey.
She could not come because she was not in the city.
Here, ”who came here”, “When the rain stopped” and “because she was not in the city” are subordinate clauses as they cannot stand alone as sentences and are dependent on the independent clauses in the mentioned sentences.এখানে, ”who came here”, “When the rain stopped” এবং “because she was not in the city” হল subordinate clause কারণ তারা পৃথক sentence হিসেবে ব্যবহৃত হতে পারে না এবং উল্লেখিত sentence গুলোর independent clause এর উপর নির্ভরশীল ।
Dependent Clause can be again divided into three types.:
Dependent Clause কে আবার তিন ভাগে ভাগ করা যায়।:
These types are discussed below.
এই প্রকারগুলো নিম্নে বর্ণিত হলো ।
Noun Clause:
The clause which can replace any noun in a sentence and act as a subject, object or complement is called noun clause.যে clause একটি sentence এ যেকোন noun এর পরিবর্তে বসে এবং subject, object বা complement হিসেবে ভূমিকা পালন করে তাকে noun clause বলে ।
Example:
The book I bought yesterday was really helpful to complete my assignment. Or What I bought yesterday was really helpful to complete my assignment.
Here “What I bought yesterday” is a noun clause acting as the subject.এখানে “What I bought yesterday” একটি noun clause যা subject হিসেবে কাজ করছে।
I did not know that she is coming.
Here “that she is coming” is the noun clause acting as the object.এখানে “that she is coming” একটি noun clause যা object হিসেবে কাজ করছে।
I am sad that you are leaving tomorrow.
Here “that you are leaving tomorrow” is a noun clause acting as an adjective complement because it answers the question “why am I sad?”এখানে “that you are leaving tomorrow” একটি noun clause যা adjective complement হিসেবে কাজ করছে কারণ এটি “আমি কেন দু:খিত” এই প্রশ্নের উত্তর দিচ্ছে ।
Adjective or Relative Clause:
The clause which describes a noun just like an adjective is called adjective or relative clause.যে clause একটি nounকে একটি adjective এর মত বর্ণনা করে তাকে adjective বা relative clause বলে।
Adjective clauses are of two types:
i. Restrictive Clause:
The adjective clause which specifies or restricts the noun is called restrictive clause.যে adjective clause কোন nounকে বিশেষভাবে নির্দিষ্ট করে বোঝায় তাকে restrictive clause বলে ।
Example:
The building that they build in Dhanmondi sold for five
Here, “that they build in Dhanmondi” is a restrictive clause because it is specifying the building. It is also implied that there could be several buildings.ii. Nonrestrictive Clause:
The adjective clause which adds extra information about an already specific noun is called nonrestrictive clause.যে adjective clause আগে থেকে নির্দিষ্ট কোন noun সম্পর্কে বাড়তি কোন তথ্য দেয় তাকে nonrestrictive clause বলে ।
Example:
The building, which they build in Dhanmondi, sold for five
Here “which they build in Dhanmondi” is a nonrestrictive clause because it is specifying the building which is already specified by a comma. It is also specified here that there is only one building to talk about.Adverb Clause:
An adverb clause expresses where, when, how and why something occurs.একটি adverb clause কোথায়, কখন, কিভাবে এবং কেন কোনকিছু ঘটে তা বোঝায় ।
Example:
I will meet you when I have completed all my assigned tasks.
Here “when I have completed all my assigned tasks” is an adverb clause as it is expressing when I will meet you.এখানে “when I have completed all my assigned tasks” একটি adverb clause কারণ এটা বোঝাচ্ছে, কখন আমি তোমার সাথে দেখা করব ।
——————————————————————
Phrases Definition:
A phrase is a group of words having no subject and finite verb which gives meaning to a sentence.
Phrase একটি শব্দগুচ্ছ যাতে কোন subject এবং finite verb থাকে না ও যা একটি sentence কে অর্থপূর্ণ করে তোলে।Example:
He is indeed a man of parts.
Life is not a bed of roses.
She has no kith and kin
The words in bold letters don’t have any subject and finite verb but still giving the sentence a meaning. They are phrases.Bold অক্ষরের শব্দগুলোর কোন subject এবং finite verb নেই কিন্তু তাও sentenceটিকে একটি অর্থ দিচ্ছে। এগুলো phrase।
Types of Phrases:
There are generally nine types of phrases (Phrase সাধারণত: নয় ধরনের):Noun Phrase.
Verb Phrase
Adverbial Phrase
Adjective Phrase
Prepositional Phrase
Conjunctional Phrase
Interjectional Phrase
Participial Phrase
Absolute Phrase
Noun phrase তিন ধরনের হয়:Appositive Phrase
Gerund Phrase
Infinitive Phrase.
Noun Phrase:
The group of words that perform the task of a noun is called Noun Phrase. Noun phrases are of three types:যে শব্দগুচ্ছ noun এর কাজ করে তাকে Noun Phrase বলে। Noun phrase তিন ধরনের হয়:
i. Appositive Phrase:
A noun phrase that renames another noun, not technically modifies it is called an appositive phrase.যে noun phrase অন্য একটি nounকে নতুন করে নাম দেয়, কৌশলগতভাবে বর্ণনা করে না তাকে appositive phrase বলে।
Example:
Nachiketa, my favorite singer, is coming to Dhaka.
ii. Gerund Phrase:
A noun phrase with a gerund as its head is called a gerund phrase.যে noun phrase এর শুরুতে gerund যুক্ত থাকে তাকে gerund phrase বলে।
Example:
I love listening to music.
iii. Infinitive Phrase:
An infinitive phrase refers to a noun phrase containing an infinitive at the beginning.যে noun phrase এর শুরুতে একটি infinitive থাকে তাকে infinitive phrase বলে।
Example:
I love to listen to music.
Verb Phrase:
The group of words that perform the task of the verb is called Verb Phrase. A verb phrase has more than one verbs, one is a principal verb, and others are auxiliary verbs, such as am, is, are, was, were, be, being, have, had, has, shall, should, etc.যে শব্দগুচ্ছ verb এর কাজ করে তাকে Verb Phrase বলে। একটি verb phrase এ একাধিক verb থাকে, একটি মূল verb এবং অপরগুলো সাহায্যকারী verb, যেমন, am, is, are, was, were, be, being, have, had has, shall, should, প্রভৃতি।
Example:
I was reading my favorite book yesterday.
They were going to the concert.Adverbial Phrase:
The group of words that perform the task of the adverb is called Adverbial Phrase. An adverbial phrase also has other words apart from adverbs such as noun, verb, preposition, and modifiers which function like an adverb in the sentence.যে শব্দগুচ্ছ adverb এর কাজ করে তাকে Adverbial Phrase বলে। একটি adverbial phrase এ adverb ছাড়াও অন্যান্য শব্দ যেমন: noun, verb, preposition এবং modifiers থাকে যা sentence এ adverb এর কাজ করে।
Example:
I came here
Once upon a time, he lived here.
She said it in a polite way.
Adjective Phrase:
The phrase that performs the function of an adjective is called Adjective Phrase.যে phrase adjective এর কাজ করে তাকে Adjective Phrase বলে।
Example:
The girl is always full of life.
She is slow and steady.
This rule is now null and void.
Prepositional Phrase:
The phrase which has a preposition as its head and functions as an adjective, adverb or noun in a sentence is called a prepositional phrase. Generally, a prepositional phrase starts with a preposition and ends with a noun or pronoun.যে phrase এর শুরুতে একটি preposition থাকে এবং যা একটি sentence এ adjective, adverb বা noun এর কাজ করে তাকে prepositional phrase বলে। সাধারণত: একটি prepositional phrase একটি preposition দিয়ে শুরু হয় এবং একটি noun বা pronoun দিয়ে শেষ হয়।
Example:
The students with whom I met at the varsity were friendly.
The salesman sells from door to door.
We are on the way to Dhaka.
Conjunctional Phrase:
The phrase which functions as a conjunction is called a conjunctional phrase.যে phrase একটি conjunction এর মত কাজ করে তাকে conjunctional phrase বলে।
Example:
We started our journey as soon as the rain stopped.
Please come as quickly as you can.
She is not only magnificently gorgeous but also brilliantly intellectual.
Interjectional Phrase:
The phrase which functions like an interjection is called an interjectional phrase.যে phrase একটি interjection এর মত কাজ করে তাকে interjectional phrase বলে।
Example:
What a miracle! She has come to the program.
My goodness! What have you done?
For heaven’s sake! Don’t go there.
Participial Phrase:
A phrase which has a present or past participle as its head is called a participial phrase.যে phrase এর শুরুতে একটি present বা past participle থাকে তাকে participial phrase বলে।
Example:
The women sitting by the river were gossiping.
Coming home, I came to know the truth.
She was drinking water in a glass made of stone.
Absolute Phrase:
The phrase which has a subject but no finite verb and modifies the whole sentence, not a noun is called an absolute phrase.যে phrase এর একটি subject আছে কিন্তু কোন finite verb নেই এবং যা সম্পূর্ণ sentenceটিকে মূল্যায়ন করে শুধু একটি noun কে নয়, তাকে absolute phrase বলে।
Example:
My friend finally coming back to this country, I will be able to share my thoughts and idea with her.
Her arrival at the last moment, we all were relieved from tension.************************************************************
-

Make Question with ‘How’
How question? ‘How’ is a very useful question word. The Wh-word ‘how’ can talk about a lot of different things. Let’s look at some of the ways it can be used.
**Structure : 1)Wh-word ‘How’/phrase
2)A-uxiliary verb
3)S-ubjecet
4)M-ain verb / Infinitive
( Four steps must be in this sequence)
★’How’ qu-estion specifically used ‘ Four’ common types of how.
For example :
1)’ How + much ‘ is asking you about a uncountable (singular) nouns.
Ex. water, money,time, coffee, sugar, love, English etc.
2) ‘ How + many’ is asking you about a countable (plural) nouns.
Ex..Apples, oranges, bags,cars,peoples, pens, cats etc.
3)’ How + adjective’ is asking you to say the quantity or degree of the adjective.
Ex..How+ old /hot, good serious /difficult/ far/tall/ high /big/deep/wide/cold/large etc.
4) ‘ How + adverb’ is asking you to say the quantity of the adverb.
Ex..’ How+ often/well/long/quickl /quietly /deeply /widely /
highly /largely /coldly /nicely/ closely etc.★1)How + much + uncountable (singular) nouns:
অর্থাৎ How much শব্দটির সাথে uncountable (অগননীয়)) nouns (বিশেষ্য) যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরী করতে হয়। যেমন :
How much time (কতটুকু সময়),How much tea ( কতটুকু চা),How much love ( কতখানি ভালোবাসা)।
Time, tea, love এই noun গুলোকে গননা করা যায় না তবে measure বা পরিমাপ করা যায়। যেমন:How much = Amount of Non countable nouns.
1) How much time does she have?= তার (স্ত্রী)কতটুকু সময় আছে?
2) How much tea does she drink?= সে কতটুকু চা পান করে ?( she drink a lot)
3) How much do you love me ?= কতটুকু ভালোবাস আমাকে? ( A lot of)
4) How much water does he drink a day?= সে (পুরুষ) একদিনে কতটুকু পানি পান করে?
5)How much sugar should I put in your coffee? = তোমার কফিতে আমি কতটুকু চিনি দিবো?
6)How much milk do they need?= তাদের কতটুক দুধ প্রয়োজন? (two liter)
7) How much price is this shirt?= এই সার্টের মূল্য কত? ( Nine hundred)
8) How much coffee would you like? = তুমি কতটুকু কফি চাও?( A lot of)
★2) How + many + plural countable nouns :
অর্থাৎ How many শব্দটির সাথে countable বা গননা করা যায়, এমন যেকোন plural (বহুবচন) noun যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরি করতে হয়।
যেমন: How many + books (কতগুলো বই), How many peoples (কতজন লোক ), How many apples ( কতটি আপেল)। ‘Books, Peoples, apples ‘ এসব শব্দগুলো count বা গননা করা যায় এবং শব্দগুলোর শেষে s যুক্ত করে plural করা হয়েছে। যেমন:How many? = number of countable nouns
1) How many books do you read in year?= বছরে তুমি কতটি বই পড়ো?( nine)
2)How many people are there?= এখানে কতজন লোক? ( fifteen)
3) How many apples did he bought? = সে ( পুরুষ) কতগুলো আপেল ক্রয় করেছিলো?
4) How many brothers do they have?= তাদের কতজন ভাই আছে?( four)
5) How many shoes does she buy? সে (স্ত্রী) কয়টি জুতা ক্রয় করেছে?
6) How many languages do you speak? = আপনি কতগুলো ভাষায় কথা বলেন ? (two)
7) How many teachers are there in this school? = এই স্কুলে কতজন শিক্ষক আছে?(ten)
8) How many rooms would you like to reserve? = আপনি কয়টি রুম রিজার্ভ করতে চান? ( five rooms)
9) How many total children will be with you?= আপনার সাথে সবমিলিয়ে কয়টি বাচ্চা থাকবে?(Six)
10) How many days would you like the room for? আপনি কয়দিনের জন্য রুমটি চাচ্ছেন?**Tips -1 : প্রশ্নবাচক বাক্যে কারো কিছু ”আছে” বুজালে Subject এর পরে ”have” বসে। যেমন:
1)How many brothers do you have?= তোমার কয়জন ভাই আছে?( five)
2) How many cars do they have? = তাদের কয়টি গাড়ি আছে?( এই বাক্যে they হলো subjet যার পরে have ব্যবহার হয়েছে)**Tips-2 : আমরা জানি 3rd person singular ‘subject ‘এর সাথে has ব্যবহার হয় কিন্তু প্রশ্নবাচক বাক্যে does এবং doesn’t এর সঙ্গে ’have’ নিজের রূপ বদলায় না। সেজন্য তৃতীয় পুরুষের সাথে does have এবং doesn’t have ব্যবহার হয়। যেমন:
1)How many horses does she have?(three)
2) How many children does Asma have?
3) How many cars does he have? (এই প্রশ্নবাচক বাক্য subject ‘he’ হলো তৃতীয় পুরুষ এবং তার আগে helping verb does হওয়ায় subject এর সাথে have ব্যবহার হয়েছে)**Tips -3 : যখন প্রশ্নবাচক বাক্যে কোন কিছু বা কারো উপস্থিত থাকার ব্যাপারে জিঙ্গাসা করা হয় তখন countable nouns এর পরে ” are there” এবং non countable nouns (বিশেষ্যের) পরে ” is there” ব্যবহার হয়। যেমন :
1) How many airports are there in Dhaka?=ঢাকাতে কতগুলো বিমানবন্দর আছে?
2) How many friends are there in the party?= পার্টিটিতে কতজন বন্ধু আছে?
3) How many bags are there? = ওখানে কতটি ব্যাগ আছে?
4) How much milk is there in the bowl?= বাটিতে কতটুকু দুধ আছে?
5) How much love is there in her heart?= তার হৃদয়ে কতখানি ভালোবাসা রয়েছে?
6) How much money is there in your poket?
= তোমার পকেটে কতটাকা রয়েছে?
7) How much hate is there in his mind?=
তার মনে কি পরিমান ঘৃনা রয়েছে?
8) How much kindness /doubt /believe / jealousy is there in her mind?**Tips -4)a) “How many times” অর্থ কত বার । এটা কোন কাজ কতবার হয় তা জিঙ্গেস করে এবং অতীত কালের জন্য ব্যবহার হয়। ( ১ বার, ১০ বার, ২০ বার, এর উত্তরগুলো প্রায় এমনি হয়)
এবং b)How often অর্থও : কতবার কিন্তু এটা বর্তমান ও ভবিষ্যৎ কালের জন্য ব্যবহার হয়। ( প্রতি সাপ্তাহে, মাসে একবার, প্রতিদিন, উত্তরগুলো প্রায় এমন হয়)
যেমন: a) How many times did the phone ring last night? = গতরাতে ফোনটা কতবার বেজেছিল? Ans: Five times.( পাঁচ বার) b) How many times did you visit India last year? ( তুমি গতবছর কতবার ভারত ভ্রমন করেছিলে? = Ans : 4 times. ( চার বার)
How many times did he fail in exam?= সে কতবার পরিক্ষায় ফেল করেছিল? Ans:3 times)
b) : How often do you visit Parish? = তুমি কতবার প্যারিস ভ্রমন করো? Ans : Every month ( প্রতি মাসে)
How often will Jamil go out for a walk? = জামিল কতবার হাঁটার জন্য বাহিরে বের হবে?Ans : Everyday ( প্রতিদিন)
How often will you go to market?=তুমি কতবার মার্কেটে যাবে? Ans : Three days in a week.( সাপ্তাহে তিনদিন)** Tips -5 : ” How much time ” অর্থ : কত সময় কিন্তু ” How long ” অর্থ : কত সময় ধরে। যেমন:
1) How much time do you need?
= আপনার কত সময় প্রয়োজন?
2) How much time does she studying?
= সে পড়ালেখায় কত সময় অতিবাহিত করে?
3) How long have you been waiting ? = আপনি এখানে কত সময় ধরে অপেক্ষা করছেন?
★★Note: যেসব noun কে গননা করা যায় তাদেরকে Countable noun বলে। যেমন : cat, dog, car, pen, bag,book,website, mangos etc. কিন্তু যেসব noun কে গননা করা যায় না তাদেরকে Non countable noun বলে। যেমন : Fun, news,mony,time,politics,information, advice,English, oil, honey,wheat,rice,spices.
Tips : How much অগননীয় জিনিসের সঙ্গে ব্যবহার করা হয় আর How many গননীয় জিনিসের সঙ্গে ব্যবহার করা হয়। যেমন:
How much water = কতটুকু পানি।
How many books = কতগুলো বই।
★ 3) 3) How + adjective : অর্থাৎ প্রশ্নবোধক শব্দ ‘How’ এর সাথে যেকোন adjective যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরি করা যায়। যেমন : How + old (কত বড়/কত বছরের), How hot ( কতটুকু গরম), How +tall ( কত লম্বা)। Old, hot, tall শব্দগুলো adjective যা how এর সাথে যুক্ত হয়ে adjective. এর Quantity (পরিমাপ) প্রকাশ করেছে। যেমন:How +adjective -indication=samp. sentence
1) How+ old – age = how old is the building?
= দালানটির বয়স কত?(thirty – three )
2) How+ hot – warm = how hot is it?
= এটা কতটুকু গরম?
3)How + tall – height= how tall is your sister? তোমার বোন কতটা লম্বা?(about two meters)
4)How+far – distance = how far is new market from here = এখান থেকে নিউ মার্কেট কত দূর?( twenty miles far)
How far do we need to go?
= আমাদেরকে কতদূর যাওয়া প্রয়োজন?
How far is your school from here?= এখান থেকে তোমার স্কুল কতদূর?( very far?
5) How high – lofty =how high is the Eiffel Tower? আইফেল টাওয়ারের উচ্চতা কতটুকু?
6)How serious – important =How serious is he?= সে কতটা গম্ভীর?
7) How big – size = how big is this road?=এই রাস্তা কতটা বড়?
8) How fast -speed = how fast is your Internet connection? তোমার ইন্টারনেট সংযোগ কতটা দ্রুত?( very fast)
9) How deep – depth =how deep is the swimming pool? = সুইমিংপুলটা কতটুকু গভীর?
10) How cold – cool = how cold is it?= এটা কতটুকু ঠান্ডা?
11) How good – condition = how good was her health?= তার স্বাস্থ্য কতটা ভালো ছিলো?( not two good)
12)How good is Anamul’s father as a man?= একজন মানুষ হিসেবে এনামুলের বাবা কতটা
ভালো?
13) How soon will they be ready? = তারা কত দ্রুত প্রস্তুত হবে?( In about one hour)
★4) How + adverb : অর্থাৎ, প্রশ্নবাচক শব্দ “How” এর সাথে adverb যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরিবকরা যায়। যেমন : How + often ( কতবার), How + long ( কতক্ষন), How + well (কতটা ভালো)। Often, long, well শব্দগুলো হলো adverb, যেগুলো How এর সাথে যুক্ত হয়ে adverb এর quantity ( পরিমাপ) প্রকাশ করেছে।যেমন:How+ adverb – meaning =samp.sentence
1) How + often – frequency= How often do you drive the car in a day = আপনি একদিনে কতবার গাড়ীটি চালান?(Ans: twice a day)
How often does she visit London a year?=সে একবছরে কতবার লন্ডন ভ্রমন করেন?
2) How + long – duration / length(time or space) = How long was your stay in Dhaka?= ঢাকাতে তুমি কত দিন ছিলে? Ans:Two year.
How long will it take?= এটা নিতে কতক্ষন লাগবে?
How long has she been here = সে এখানে কতক্ষন আছে? Ans: Three hour.
How long did it take you to get here?= তোমার আসতে কতক্ষন লাগলো?
3) How + well – goodly = how well does Pranti know him? প্রান্তি তাকে কতটা ভালো করে চিনে/ জানে ?( not very well)
4) How + quickly – speedily = how quickly can you finish this? = তুমি কতটা দ্রুতভাবে এটা শেষ করতে পারো?
5) How + quietly – calmly = how quietly can Puspo speak? = পুষ্প কতটা শান্তভাবে কথা বলতে পারে?
6) How carefully does he drive his car? = কতটা সচেতনভাবে সে তার গাড়ী চালায়?
7) How safely do you stay in Dhaka?=
ঢাকায় তুমি কতটা নিরাপদে থাকো?
8)How loudly were they shouting?
= তারা কত জোরে চিৎকার করতেছিলো?
Note: An adjective modifies a noun or a pronoun by qualifying, specifying or describing it. Ex. nice, happy, wise loud etc.
But an adverbs modify ( describe) verbs, adjectives and other adverb.Ex.well, loudly.** Many adverbs are made by adding -ly to adjectives. EX..
adjectives+ ly =Adverbs
—————- + -= ————–
1) Sweet+ ly = sweetly
2) Loud+ ly = loudly
3) Heavy+ly = heavily
4) Bright + ly = brightly
5) Brave +ly = bravely
6) Smart+ly= smartly
7) Selfish+ly= selfishly
8) Safe + ly= safely
9) Careful +ly=carefully
10) Regular+ly=regularly
11) Close +ly = closely
12) Correct +ly= correctly★ How + other usual:
a) How + modal = অর্থাৎ, How এর সাথে modal auxiliary verb যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরি করা যায়। Can,could shall, should, will, would, may, might, must ইত্যাদি verb গুলোকে modal বলা হয়। যেমন :
1) How can I learn English quickly?
= কিভাবে আমি দ্রুত ইংরেজি শিখতে পারি?
2) How could we improve our English
= আমরা কিভাবে আমাদের ইংরেজি ভালো করতে পারবো?
3)How would you do it? = তুমি এটা কিভাবে করতে চাও?
4)How may I wait? আমি কিভাবে অপেক্ষা করতে পারি?
5) How might he go? = সে কিভাবে যেতে পারতো?
6) How can she trust me? সে কিভাবে আমাকে বিশ্বাস করতে পারে?
7) How can I thank you?= আমি কিভাবে তোমাকে ধন্যবাদ জানাতে পারি?
b) How + present tense : অর্থাৎ প্রশ্নবোধক শব্দ ” How” এর সঙ্গে, helping verb হিসেবে am, is, are, do, does, have, has, have been, has been যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরি করা যায়। যেমন:
1) How am I a honest man ? আমি কতটা সৎ মানুষ?
2) How is her married life going?
= তার বিবাহিত জীবন কেমন যাচ্ছে?
3) How are you going there?
= তোমরা সেখানে কিভাবে যাচ্ছো?
4) How do they upload photos to your website?= তারা কিভাবে তোমার ওয়েবসাইটে ছবি আপলোড করে?
5)How does this work?= এই কাজটি কেমন?
6) How have you gone there ? তুমি কিভাবে সেখানে গিয়েছো?
7) How has Pranti sang the song?
= প্রান্তি কিভাবে গানটা গেয়েছে?
8)How have you been keeping?
= কেমন যাচ্ছে আপনার?
9) How has she been staying for five years?
= পাঁচ বছর যাবৎ সে কিভাবে এখানে থাকতেছে?
10)How do you know him = তুমি তাকে কিভাবে জানো / চিনো?
11) How do we get to the new market from here? = এখান থেকে আমরা কিভাবে নিউ মার্কেট যাবো?
12) How do you know where I live?
13) How has Arisha’s life changed since her got married? বিয়ে হওয়ার পর থেকে আরিশার জীবন কতটা পরিবর্তন হয়েছে?
14)How do you know that Pranti doesn’t like him? প্রান্তি তাকে পছন্দ করে নাহ তুমি তা কিভাবে জানো?
15) How does it taste? এটার স্বাদ কেমন?
16) How does it look? এটা দেখতে কেমন?
17) How do you like my new shirt?
= আমার নতুন সার্টটা তুমি কতটা পছন্দ করো?
c) How + past tense : অর্থাৎ, অতীত কালের প্রশ্ন তৈরি করতে How এর সঙ্গে was, were, did, had, had been ইত্যাদি helping verb কে যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরি করা যায়। যেমন:
1) How was the trip? = ভ্রমনটা কেমন হলো?
2) How were they walking? = তারা কিভাবে হাঁটতে ছিলো?
3) How did you know I was in Dhaka?
= আমি ঢাকায় ছিলাম তুমি কিভাবে জানতে?
4) How had you gone London?
= সে কিভাবে লন্ডন গিয়েছিল?
5) How did they handle the conflict = তারা কিভাবে বিরোধটি মোকাবিলা করলো?
6) How was her time with Jamil last night?
গতরাতে জামিলের সাথে তার সময়টা কেমন ছিলো?
7) How did she help to escape?
= সে কিভাবে পালাতে সাহায্য করেছিলো?
8) How did they know we were here?
= আমরা এখানে ছিলাম তারা কিভাবে জানতো?
9) How did he know her name is Arisha?
= সে কিভাবে জানতো তার নাম আরিশা?
d) How + Future tense: অর্থাৎ, ভবিষ্যৎ কালের প্রশ্ন তৈরি করতে, প্রশ্নবাচক শব্দ “How” এর সঙ্গে ‘ will, will be যুক্ত করে প্রশ্ন তৈরি করা যায়। যেমন : 1) How will Anamul help him? তাকে এনামুল কিভাবে সহযোগীতা করবে?
2) How will Pranti prove it? প্রান্তি এটা প্রমান কিভাবে করবে?
3) How will their react =
তাদের প্রতিক্রিয়া কেমন হবে?
4) How will I carry it? =
আমি কিভাবে এটা বহন করবো?
5) How will you get paid?
তুমি কিভাবে দিতে পারবে?
6) How will you be going to Lakshmipur?
= আপনি কিভাবে লক্ষীপুর যাবেন?
7) How will Pranti be singing a song?
= প্রান্তি কিভাবে গান গাইবে?
8) How will they be staying in Dhaka?
= তারা কিভাবে ঢাকায় থাকবেন?- * Exception (ব্যাতিক্রমী):
a)Some ” How ” questions consists of simply a question word with a main verb. Structure : How + main verb
1) How + goes? = কিভাবে যায়?
2) How looks?= কেমন লাগছে?
3) How wants = কিভাবে চায়?
4) How played = কেমন খেলল?
5) How liked = কেমন লেগেছে?
b) How come: “How come ” phrase টি দ্বারা reason (কারন) বুজায়। যেমন:
1) How come I never see you?
=তোমাকে কেন আর দেখি নাহ?
2) How come you didn’t tell Jamil about me? = কি কারনে তুমি জামিলকে আমার ব্যাপারে বলোনি?
3) How come she mad a great mistake?
= কিভাবে সে এতবড় ভুল করলো?
- * Exception (ব্যাতিক্রমী):